Goal Detection
Brief
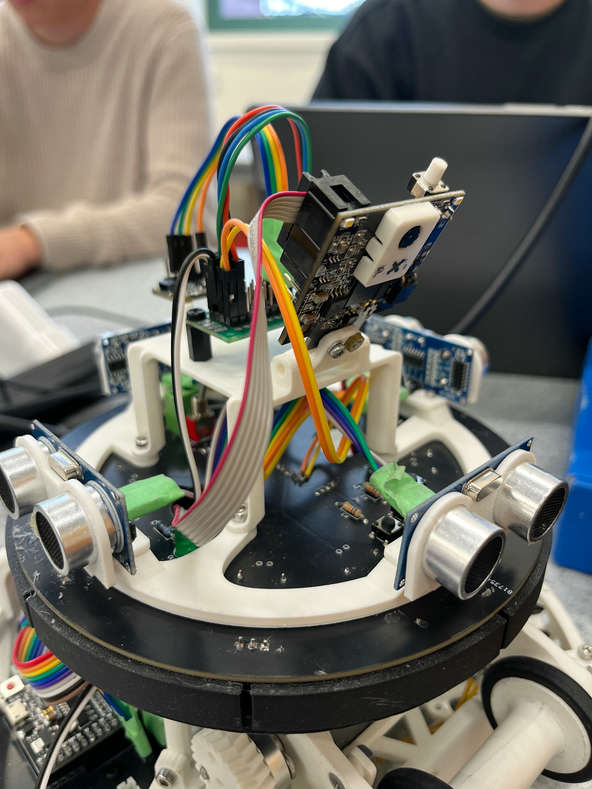
An important part of attacking is being able to detect the goal. Our robot uses a PixyCam V2 with simple blob detection to detect the coloured goals. We use this information to calculate the relative heading from the robot, as well as the distance from the goal. Together these feed into the attack logic to determine movement with the ball, and also allow for the goalie to return to its position. This enables a more advanced strategy where robots are role-fluid, being able to change as needed.
Development
The PixyCam is extremely easy to work with. Within 5 minutes you can set up goal detection too. It was as easy as just plugging the camera into the computer and dragging a rectangle around the goal on the video feed, and that's it - simple blob detection is done. The PixyCam is wired to our Arduino Mega through the ICSP headers, and the PixyCam Arduino library handles communication. Once we get the data from the camera, there are two functions we implemented, one to calculate the relative heading of the goal from the robot, as well as the distance. We researched the math for this online and got it checked by ChatGPT. Surprisingly, the distance estimation was quite accurate, with an absolute error range of ±5cm which is more than enough for our use case. This provides far more useful information for the attacker especially, rather than just shooting arbitrarily in the heading of the opponent's goal, and opens up new possibilities for strategy, as the goalie has the capability of homing.